How the CSRD will impact your company
Blog
What is the CSRD?
The Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) is new EU legislation that requires large companies to report on sustainability. The directive aims to ensure greater transparency, improve the quality of sustainability information, and enable better comparison of the information provided by companies. It is also expected to speed up the transition towards a sustainable future, thus supporting the aims of the European Green Deal including implementing the Paris Agreement. It will help stakeholders such as investors, policymakers, employees, consumers and others to evaluate companies' non-financial performance. Above all, the greatest change we expect from the CSRD is that it will lead to behavioural change within companies.
For which companies is it relevant?
The Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) is applicable to all (listed and non-listed) large companies that meet two of the following three criteria:
- >250 employees
- >40 million euros turnover
- >20 million total assets
How many companies will be impacted by the CSRD?
In Europe, 49,000 companies are expected to fall within the scope of the new directive, with more than 2,000 of them in the Netherlands. The CSRD replaces the Non-Financial Reporting Directive (NFRD) which, in comparison, required reporting by 11,600 companies in Europe, of which 115 are in the Netherlands.
When do companies need to start reporting under the new directive?
- Companies falling within the scope of the current Non-Financial Reporting Directive (NFRD) must issue a CSRD-compliant report on their 2024 fiscal year sustainability performance. We expect to see the first CSRD-compliant reports early in 2025.
- Other large companies, that meet two of the three criteria mentioned above, must issue a CSRD-compliant report on their 2025 fiscal year sustainability performance.
- Listed SMEs must start reporting their sustainability performance for the 2026 fiscal year, but may opt out until 2028. A separate standard will be developed for SMEs.
What is the structure of the new standards?
The European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS) set out the detailed disclosure requirements of the European Commission under the CSRD. The ESRS comprises 12 standards covering environmental, social and governance matters. In future, sector-specific standards will become available. Main components include double materiality, inclusion of prospective information, information about the upstream and downstream value chain and the concept of sustainability due diligence. ESRS 2, ESRS E1 and ESRS S1 are mandatory for all companies, regardless of the materiality assessment (with ESRS S1 mandatory for companies with > 250 employees). All other ESRS are only mandatory if material.
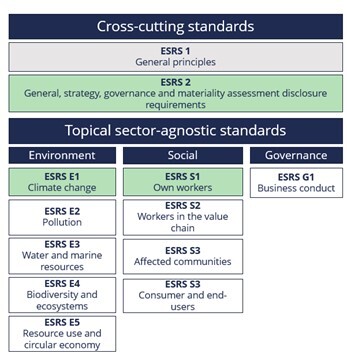
How should the sustainability report be structured?
Sustainability information should be structured as follows, to promote transparency and comparability:
| Part of the management report | ESRS | Title |
| 1. General information | ESRS 2 | General disclosures about the company |
| 2. Environmental information | ESRS E1 | Climate change |
| ESRS E2 | Pollution | |
| ESRS E3 | Water and marine resources | |
| ESRS E4 | Biodiversity and ecosystems | |
| ESRS E5 | Resource use and circular economy | |
| 3. Social information | ESRS S1 | Own workforce |
| ESRS S2 | Workers in the value chain | |
| ESRS S3 | Affected communities | |
| ESRS S4 | Consumers and end-users | |
| 4. Governance information | ESRS G1 | Business conduct |
What are the sub-topics of each sustainability matter?
The overview, below, provides a better picture of each sustainability matter and its sub-topics, giving a detailed overview of the topics on which you are required to report. Note that all companies must report on Climate Change, irrespective of the outcome of the materiality assessment.
| ESRS | Topic | Sub-topic | Sub-sub-topics |
| E1 | Climate change | • Climate change adaptation • Climate change mitigation • Energy |
|
| E2 | Pollution | • Pollution of air, water, soil, living organisms & food resources • Substances of concern & very high concern | |
| E3 | Water & marine resources | • Water withdrawals • Water consumption • Water use • Water discharges in waterbodies and in the oceans • Habitat degradation and intensity of pressure on marine resources |
|
| E4 | Biodiversity & ecosystems | • Direct impact drivers of biodiversity loss | • Climate Change • Land-use change • Direct exploitation • Invasive alien species • Pollution • Others |
| • Impacts on the state of species • Impacts on the extent & condition of ecosystems • Impacts and dependencies on ecosystem services | • Species population size • Species global extinction risk • Land degradation • Desertification • Soil sealing | ||
| E5 | Circular economy | • Resources inflows, including resource use • Resource outflows related to products & services • Waste | |
| S1 | Own workforce | • Working conditions | • Secure employment • Working time • Adequate wages • Social dialogue • Freedom of association, the existence of works councils and the information, consultation, and participation rights of workers • Collective bargaining, including rate of workers covered by collective agreements • Work-life balance • Health and safety |
| • Equal treatment and opportunities for all | • Gender equality & equal pay for work of equal value • Training and skills development • Employment and inclusion of persons with disabilities • Measures against violence and harassment in the workplace • Diversity | ||
| • Other work-related rights | • Child labor • Forced labor • Adequate housing • Privacy | ||
| S2 | Workers in the value chain | • Working conditions | • Secure employment • Working time • Adequate wages • Social dialogue • Freedom of association, including the existence of work councils • Collective bargaining • Work-life balance • Health & safety |
| • Equal treatment and opportunities for all | • Gender equality and equal pay for work of equal value • Training and skills development • The employment and inclusion of persons with disabilities • Measures against violence and harassment in the workplace • Diversity | ||
| • Other work-related rights | • Child labor • Forced labor • Adequate housing • Water and sanitation • Privacy | ||
| S3 | Affected communities | • Communities’ economic, social and cultural rights | • Adequate housing • Adequate food • Water and sanitation • Land-related impacts • Security-related impacts |
| • Communities’ civil and political rights | • Freedom of expression • Freedom of assembly • Impacts on human rights defenders | ||
| • Rights of indigenous communities | • Free, prior and informed consent • Self-determination • Cultural rights | ||
| S4 | Consumers and end users | • Information-related impacts for consumers and/or end-users | • Privacy • Freedom of expression • Access to (quality) information |
| • Personal safety of consumers and/or end-users | • Health and safety • Security of a person • Protection of children | ||
| • Social inclusion of consumers and/or end-users | • Non-discrimination • Access to products and services • Responsible marketing practices | ||
| G1 | Business conduct | • Corporate culture • Protection of whistle-blowers • Animal welfare • Political engagement and lobbying activities • Management of relationships with suppliers including payment practices | |
| • Corruption and bribery | • Prevention and detection including training • Incidents |
Where can I find more information?
For more information, see all ESRS here. Each European Sustainability Reporting Standard will guide you through the disclosure requirements in detail.
We are also happy to help you!
Contact us, without obligation, for:
- An introductory conversation
- A CSRD quick scan of the disclosure requirements and your current report
- Help in setting up your sustainability report
- How to work toward CSRD compliance and behaviour change.
Please reach out to
Ulrike@toscatribe.nl (+31 651 072 464)
or
Nicolette@toscatribe.nl (+31 653 288 506).
We look forward to helping you.
Back to news




















